As described in Hydraulic Pumps 101, hydraulic pumps are among the most necessary components in a hydraulic system. They convert mechanical energy into hydraulic power.
Hydrostatic pumps, or positive displacement pumps, create this power with very little quantity or velocity of the liquid, making them the subject of many questions about their functionality.
In general, positive displacement pumps work by displacing liquid by trapping it between pumping elements and a stationary casing. The design of PDPs can include gears, lobes, rotary pistons, vanes, or screws.PDPs can be categorized as reciprocating or rotary. Rotary positive displacement pumps use rotating cogs or gears to transfer fluids rather than the backward-and-forward motion of reciprocating pumps.
To know how PSDs operate further, let’s answer a few common questions among hydraulics distributors and end-users:
- How do hydraulic gear pumps work?
- How do hydraulic vane pumps work?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
How Hydraulic Gear Pumps Work
Gear pumps are the simplest example of a rotary positive displacement pump.
Their straightforward design can include either internal or external gears, lobes, or screws.
Regardless of design, the rotating action of teeth or grooves creates a liquid seal and suction at the pump inlet. Fluid is drawn into the pump, enclosed within the rotating teeth, and transferred to the discharge.
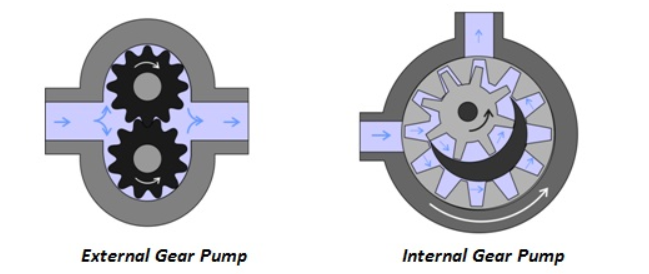
External Gear Pumps rotate, trapping fluid between the teeth and moving it from the inlet to the casing.
Internal Gear Pumps work similarly, but two interlocking gears of different sizes trap and disperse fluid as one gear rotates inside the other.
Gear pumps have these advantages:
- Simple design makes them less complex, lower in cost, and easier to maintain
- Creates a high pressure up to 3,000 psi
- Able to pump viscous fluids, unlike centrifugal pumps
- They are efficient, with low chances of leakage and contamination
- Can run in two directions for loading and unloading
- Gears can not tolerate abrasive fluids
- They are noisy
- Their limited size cannot handle large bulk flow rates
How Hydraulic Vane Pumps Work
A vane pump, as its name implies, is a rotary displacement pump that consists of vanes mounted on a cylindrical rotor.Vane pumps work similarly to gear pumps, creating suction and drawing fluid from an inlet with the rotation of the vanes instead of gears, compressing and discharging the enclosed fluid at the outlet.
This set of paddle-like vanes is mounted radially on a cylindrical rotor and creates the compartments that trap and transport the fluid through the system. The vanes can be sliding or flexible.
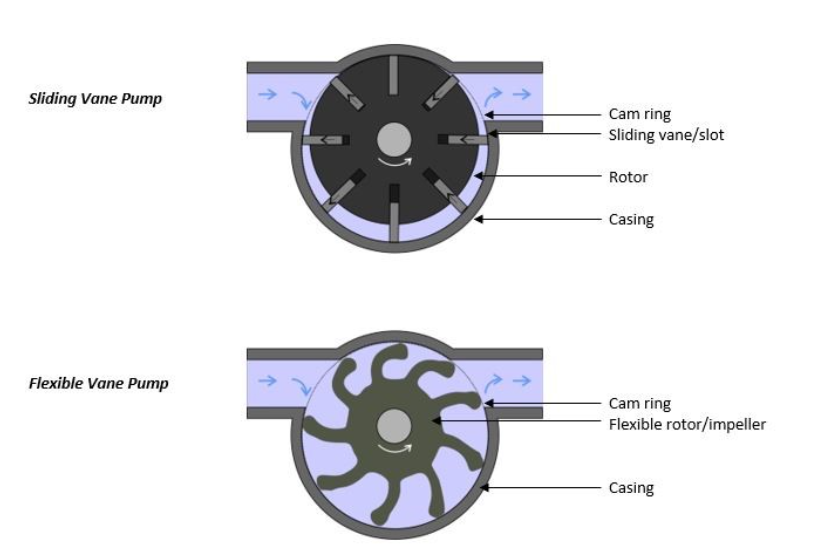
In a flexible vane pump, the rotor is made from a flexible material, shaped with several lobes that maintain contact with the pump casing. The rotor is offset and slightly larger than the casing, bending and creating compartments that expand at the inlet for suction and compress at the discharge outlet.
With the sliding action and contact with the casing, vane pumps are ideal for pumping low to medium-viscosity fluids.
Advantages of vane pumps include:
- Good suction characteristics
- Accurate and low maintenance
- Lower noise due to smooth operation and low pulsation
- No internal metal-to-metal contact
- Self-compensates for wear through vane extension
- Can handle thin liquids (or run dry for periods) at relatively high pressures
Disadvantages of vane pumps include:
- Complex housing and many parts
- Requires a shaft seal or magnetic coupling, which can be a source of leaks
- Pulsation may be a problem at low speeds
- Not suitable for high-pressure or high-viscosity applications
- Not good for?abrasive applications
Hydraulic Parts Source is a great resource to fulfill your hydraulic pump repair and replacement needs. Visit Hydparts.com for a full list of pumps we service, or contact us to get a quote.
Tags
Posts
2024
August
2023
Need a Quality Supplier? HPS Checks All the Marks
[08/29/24 04:12 PM]
Digitization & Hydraulics
[08/29/24 03:45 PM]
February
Meet Our New Hydraulic Test Stand: Part 2
[02/15/24 02:50 PM]
Remanufacturing Benefits for End-Users
[02/01/24 03:04 PM]
January
December
2022
Hydraulic Systems and Their Components: An Overview
[12/20/23 12:27 PM]
Overfilling Hydraulic Fluid Can Cause Issues, Too
[12/08/23 01:18 PM]
November
Branded Gifts for Commuting Hydraulics Clients
[11/09/23 08:41 PM]
Diagnosing Pump Problems on Construction Equipment
[11/08/23 01:42 PM]
October
The Useful Complexity of Proportional Control Valves
[10/25/23 09:11 PM]
FAQs: Let’s Talk About Hydraulic Pumps
[10/23/23 08:25 AM]
Hydraulics System Corrosion FAQs
[10/11/23 01:00 PM]
September
August
5 Ways Inside Reps Can Boost Hydraulics Sales
[08/13/23 03:54 PM]
Positive Displacement Pump FAQs: How Do Hydraulic Vane and Gear Pumps Work?
[08/10/23 06:15 PM]
The Value of Hydraulic Pressure Relief Valves
[08/02/23 05:26 PM]
July
June
May
Hydraulic Parts Source is So Much More Than Pumps, Valves, and Motors
[05/30/23 12:09 PM]
How Does a Hydrostatic Pump Work?
[05/15/23 11:07 AM]
April
How Do Directional Control Valves Work?
[04/27/23 10:37 AM]
From Valves to Motion: Knowing How a Cylinder Works to Move a Hydraulic System
[04/14/23 10:23 AM]
March
HPS Troubleshooting Tactics: Common Hydraulic Valve Issues
[03/15/23 10:47 AM]
What Happens When Hydraulic Parts Suppliers & Distributors Join Forces?
[03/15/23 10:04 AM]
February
January
December
November
October
September
August
July
June
2021
Denison’s Innovative Beginnings Show Through in Quality, Flexible Parts
[06/20/22 06:38 PM]
Our Products: Get to Know True Blue Vickers
[06/06/22 06:30 PM]
May
Pascal’s Principle and the Origin of Hydraulics
[05/31/22 06:25 PM]
Avoiding Devastating Cavitation Damage
[05/03/22 06:16 PM]
April
Hydraulic Parts: How to Make Green Choices
[04/18/22 06:09 PM]
Hydraulic System Hazards: Avoiding Safety Issues from the Beginning
[04/05/22 05:58 PM]
March
Motors 101: Hydraulics at Work
[03/21/22 07:00 PM]
Valves 101: It’s All About Control - and Some Other Need-to-Know Facts
[03/07/22 06:53 PM]
February
January
December
November
2020
Promotional Gift Ideas for Fluid Power Distributors to Unwrap Marketing Potential
[11/29/21 10:00 AM]
Need-to-Know Fluid Power Facts: The 5 W's of Hydraulic Oil Viscosity
[11/29/21 09:32 AM]
How to Close the Sales Gap & Increase Revenue: Part 2
[11/08/21 08:06 PM]
October
September
August
July
June
Change Filter Elements to Avoid a Hydraulic System Nightmare
[06/07/21 05:02 PM]
5 Sources of Hydraulic Fluid Contamination (and How to Address Them)
[06/01/21 04:09 PM]
April
How to Win Back Lost Customers: 5 Steps for Fluid Power Distributors
[04/19/21 04:03 PM]
7 Outside Sales Strategies to Drive Fluid Power Revenue
[04/05/21 03:54 PM]
March
4 Reasons Fluid Power Distributors Should Consider Promotional Gifts
[03/16/21 03:48 PM]
Hydraulic System Corrosion: 3 Causes & 6 Prevention Tips
[03/10/21 03:42 PM]
February
Setting and Troubleshooting Relief Valves in Hydraulic Systems
[02/23/21 03:36 PM]
When & How to Replace a Hydraulic Pump Hose Assembly
[02/08/21 03:26 PM]
January
December
3 Directional Control Valve Problems & Fixes
[12/15/20 12:22 PM]
3 Ways to Align a Hydraulic Pump
[12/01/20 12:15 PM]
November
Why Are My Hydraulic Seals Failing? 6 Common Causes
[11/16/20 12:09 PM]
8 End-User Tips for Choosing a Hydraulic Fluid Power Products Distributor
[11/02/20 12:05 PM]
October
September
8 Checks for Restarting Hydraulic Pumps After Long Shutoff
[09/29/20 11:45 AM]
6 Key Hydraulic Product Distributor Strengths
[09/21/20 11:38 AM]
8 Things to Check When Your Hydraulic Pump Stops Flowing
[09/01/20 09:47 AM]
August
3 Common Causes of Noisy Pumps and What to Check
[08/17/20 09:34 AM]
Old Cores: The Key to New Revenue for Fluid Power Distributors
[08/03/20 09:01 AM]
May

